After a thorough examination of the patient’s anatomical structures of the oral cavity, the doctor makes a diagnosis.
The proper diagnosis dictates the choice of treatment.
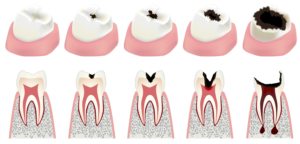
- Spot stage caries
- Surface stage caries;
- Caries middle stage;
- Deep caries stage;
- Caries complications (pulpitis, periodontitis)
Spot stage – a white spot appears on the tooth, which indicates demineralization of the tooth enamel. The treatment is carried out based on preventive measures: compliance with oral hygiene, regular brushing of the teeth at least twice a day, the use of special therapeutic and preventive tooth pastes with a high content of fluoride and calcium.
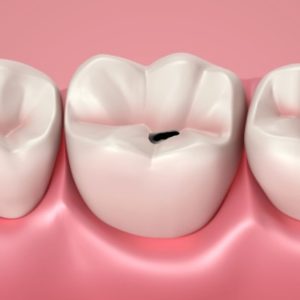 Superficial / medium caries – a small / medium cavity appears in the tooth. The tooth is sensitive to sweets, hot and cold. The teatment of uncomplicated forms of caries is a thorough cleaning of the cavity and filling the tooth.
Superficial / medium caries – a small / medium cavity appears in the tooth. The tooth is sensitive to sweets, hot and cold. The teatment of uncomplicated forms of caries is a thorough cleaning of the cavity and filling the tooth.
If caries has developed, it is important to consult your dentist as soon as possible for treatment. Deep caries is more difficult to treat and takes longer, it can also cause serious complications.
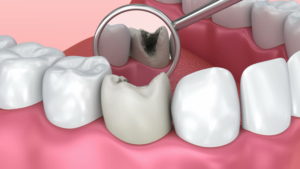 Deep caries – is the last stage of the carious process. The dental cavity is quite deep, characterized by a large damage to the hard tissues of the tooth, which affects the deep layers of the dentine. The tooth is painful and reacts to hot and cold. In case of deep caries, only a very thin layer of insufficient dentin remains between the bottom of the caries cavity and the tooth pulp. Cariogenic microorganisms can penetrate deep into healthy dentin.
Deep caries – is the last stage of the carious process. The dental cavity is quite deep, characterized by a large damage to the hard tissues of the tooth, which affects the deep layers of the dentine. The tooth is painful and reacts to hot and cold. In case of deep caries, only a very thin layer of insufficient dentin remains between the bottom of the caries cavity and the tooth pulp. Cariogenic microorganisms can penetrate deep into healthy dentin.
Even when a healthy dentin layer is present, it can not be guaranteed that the tooth pulp is not contaminated. Deep caries can be treated in several stages starting with a thorough cleaning temporary filling, and then sealing with a permanent one. In cases when the dental pulp is damaged, an endodontic treatment is needed, i. e. root canal treatments.
 Cervical caries is considered one of the most dangerous types of caries, which destroys the tooth at the very base, affecting all the canals of the tooth. Most often this type of caries affects people over 30. Diagnosis of cervical caries is not difficult. White chalk spots can be seen in the mirror by the patient, especially if the surface of the teeth are dry.
Cervical caries is considered one of the most dangerous types of caries, which destroys the tooth at the very base, affecting all the canals of the tooth. Most often this type of caries affects people over 30. Diagnosis of cervical caries is not difficult. White chalk spots can be seen in the mirror by the patient, especially if the surface of the teeth are dry.
The treatment of cervical caries does not differ from the treatment of an ordinary caries. If the treatment is delayed, the decay process,and endodontic treatment is necessary (i.e. root canal treatment).
Root caries – is a carious process located on the surface of the dental root near the marginal resin. This type of caries is a pretty insidious disease. It can be both an independent disease and a next stage of the development of the cervical caries. Formally, it was called “cement caries”. In general, it is seen mainly in mature patients
Fissure caries —is a lesion of fissures of the tooth, anatomical grooves located on its chewing surface. The presence of plaque in the fissures leads to the appearance of an early caries of the enamel, which is called fissure caries. Enamel caries can develop slowly, gradually turning from a small caries to a large one. In the early stages of fissure caries, its development may still be reversible. With the deterioration of the conditions, the tooth enamel in the fissure becomes loose.
Fissure caries treatment is necessary even in the case of milk teeth, although many parents do not consider it necessary, since “they will fall out anyway”.
When conditions improve, the enamel caries retreats, and it becomes strong again. Most often it affects the teeth in childhood, because at this age the mineralization of the tooth enamel is still quite weak, the oral hygiene is not thorough enough, and the structure of the fissures contributes to the accumulation of food debris in them and the formation of the microbial environment and dental plaque. Caries of this type is fairly easy to determine. The enamel darkens, and in the fissure area on the chewing surface, the tooth begins to collapse. Fissure caries can also be manifested by bouts of pain. In addition, the teeth become more sensitive to temperature changes (this occurs as a result of damaged tooth tissue).
It is important to remember that if he appeared in caries, he himself will not disappear. Only a timely visit to a specialist and effective treatment of dental caries will help to avoid the progression of the disease.